Installing a Samba AD/DC Service
Introduction
The Samba service can function as an AD/DC (Active Directory/Domain Controller). It is sufficiently mature to be reliably used for managing users and systems within networks running Windows 10/11 and Linux operating systems. It is recommended that this server be dedicated exclusively to authentication and authorization services, and not provide file or print services; these responsibilities should be assigned to domain member servers.1
Parameter Configuration
SO: Linux - Ubuntu Server
Hostname: dc1
Local IP Address: 192.168.0.51
Authentication Domain: svgenebank.lan
Warning:
When selecting the domain name, if no purchased domain is available, the standards outlined in RFC 6762 and RFC 8375 must be observed.
Since the server will function as a DC and AD (Domain Controller and Active Directory) in a residential environment, it is recommended to use the domain "home.arpa" (see RFC 8375). In a non-residential environment, select a domain in accordance with section G of RFC 6762.
If a domain has been purchased, use subdomain.domain_name.domain as the authentication domain.
Initial Verification
To begin, verify and configure certain server settings:
- Ensure that the server has the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) assigned:
- This can be configured during installation:
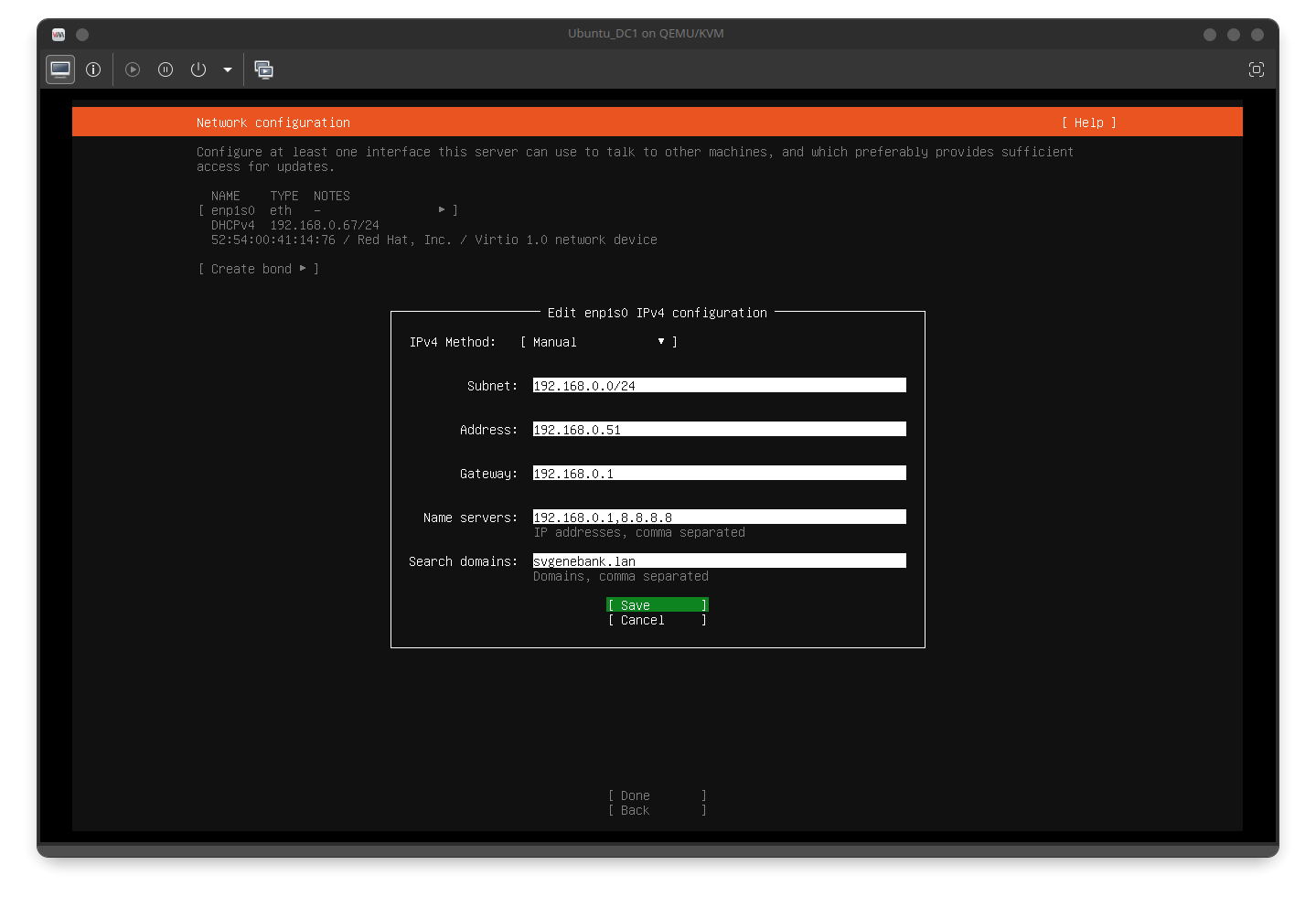 and
and
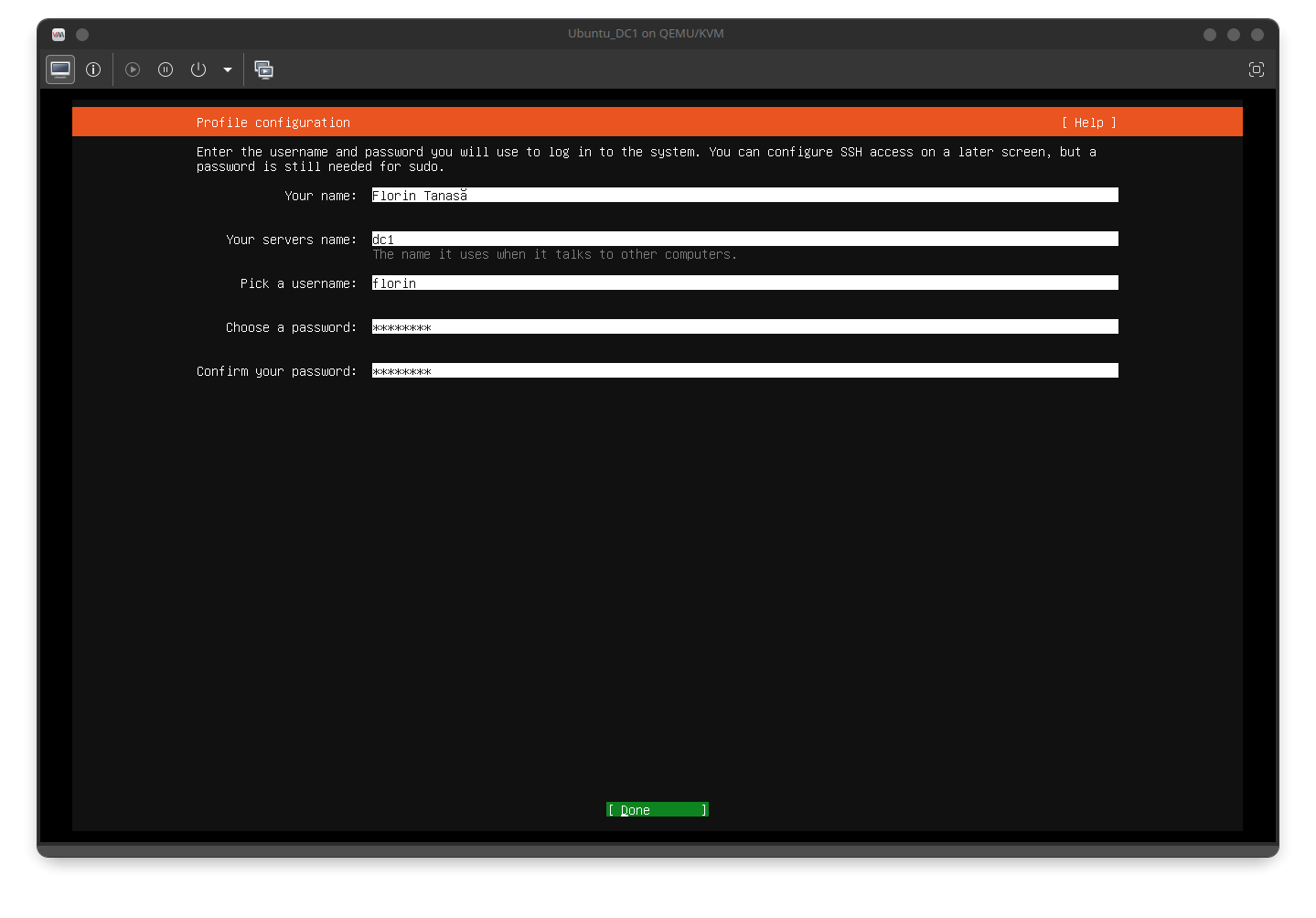
- For an existing system, use the hostnamectl command:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname dc1Next, configure the IP address and domain controller hostname in /etc/hosts to ensure proper domain name resolution:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo nano /etc/hostsComment out or remove the line containing 127.0.1.1 dc1 and add local_ip_address hostname.domain alias. The file
/etc/hostswill appear as follows in the final configuration:
- This can be configured during installation:
127.0.0.1 localhost
#127.0.1.1 dc1
192.168.0.51 dc1.svgenebank.lan dc1
# The following lines are recommended for IPv6-capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allroutersAfter configuration, verify the following:
florin@dc1:~$ hostname
dc1
florin@dc1:~$ hostname -d
svgenebank.lan
florin@dc1:~$ hostname -f
dc1.svgenebank.lanIt is critical that the clocks of all computers in the network are synchronized. Check and select the appropriate time zone:
florin@dc1:~$ timedatectl
Local time: Sat 2025-05-17 11:15:05 UTC
Universal time: Sat 2025-05-17 11:15:05 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2025-05-17 11:15:05
Time zone: Etc/UTC (UTC, +0000)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: active
RTC in local TZ: no
florin@dc1:~$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Bucharest
florin@dc1:~$ timedatectl
Local time: Sat 2025-05-17 14:16:25 EEST
Universal time: Sat 2025-05-17 11:16:25 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2025-05-17 11:16:25
Time zone: Europe/Bucharest (EEST, +0300)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: active
RTC in local TZ: noThe line System clock synchronized: yes confirms that the clock is synchronized.
Because Ubuntu uses a service called systemd-resolved for DNS resolution, it is necessary to stop and disable this service, remove the symbolic link /etc/resolv.conf, and create a new /etc/resolv.conf file where the DNS server addresses will be specified:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl disable --now systemd-resolved
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.freedesktop.resolve1.service".
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/sysinit.target.wants/systemd-resolved.service".
florin@dc1:~$ ls -lah /etc/resolv.conf
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 39 Feb 16 20:58 /etc/resolv.conf -> ../run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf
florin@dc1:~$ sudo rm /etc/resolv.conf
florin@dc1:~$ sudo touch /etc/resolv.conf
florin@dc1:~$ ls -lah /etc/resolv.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 07:20 /etc/resolv.confProceed to edit the file /etc/resolv.conf as follows:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo nano /etc/resolv.confWithin the file, define the DNS server IP addresses used by the domain controller dc1:
# Samba server DC-AC
nameserver 192.168.0.51
# Internet name server
nameserver 8.8.8.8
# My Samba domain name
search svgenebank.lanFinally, restart the server (machine or computer):
florin@dc1:~$ sudo rebootAfter restarting, verify the internet connection and confirm that the machine with the AD-DC is detected:
florin@dc1:~$ ping -c3 google.ro
PING google.ro (172.217.169.99) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from sof02s31-in-f3.1e100.net (172.217.169.99): icmp_seq=1 ttl=112 time=26.0 ms
64 bytes from sof02s31-in-f3.1e100.net (172.217.169.99): icmp_seq=2 ttl=112 time=25.9 ms
64 bytes from sof02s31-in-f3.1e100.net (172.217.169.99): icmp_seq=3 ttl=112 time=26.0 ms
--- google.ro ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 25.944/25.994/26.038/0.038 ms
florin@dc1:~$ ping -c3 dc1
PING dc1.svgenebank.lan (192.168.0.51) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from dc1.svgenebank.lan (192.168.0.51): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.035 ms
64 bytes from dc1.svgenebank.lan (192.168.0.51): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.062 ms
64 bytes from dc1.svgenebank.lan (192.168.0.51): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.062 ms
--- dc1.svgenebank.lan ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2055ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.035/0.053/0.062/0.012 msSamba Installation
Samba can be installed from source by following the instructions here or by using the distribution packages , in this case for Ubuntu.
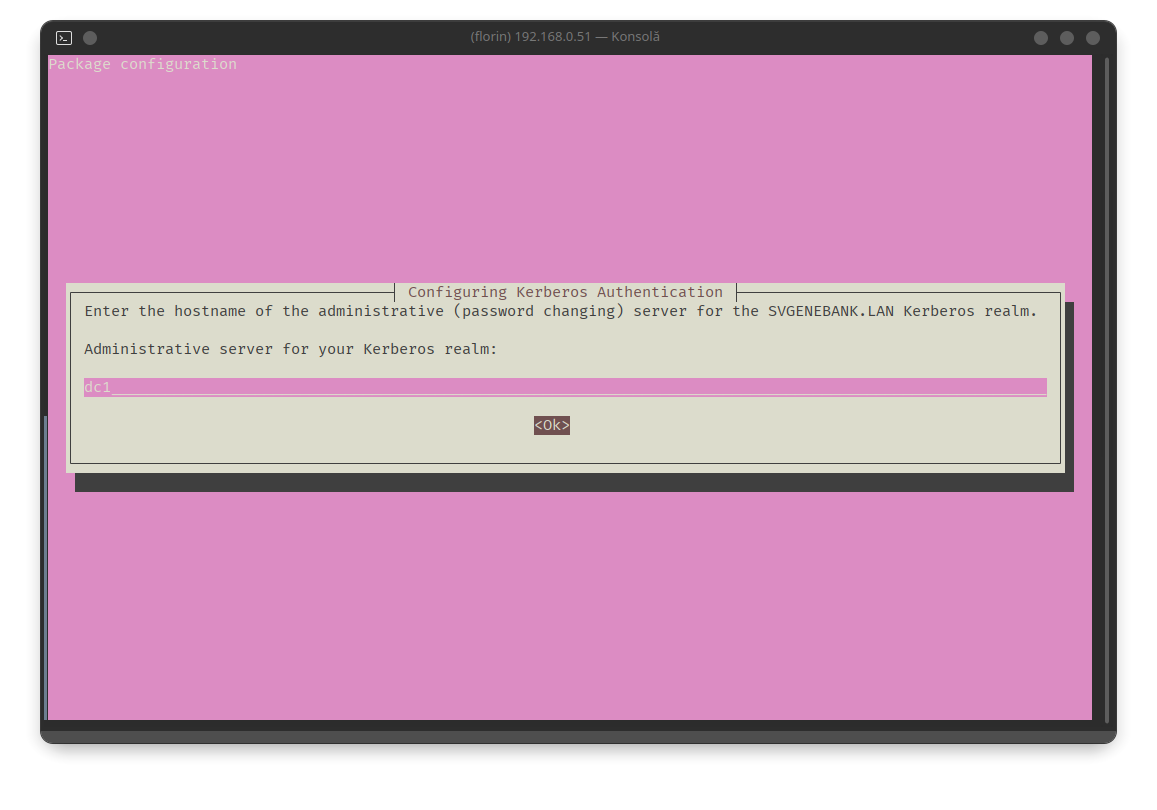
sudo apt install -y acl attr samba samba-dsdb-modules samba-vfs-modules smbclient winbind libpam-winbind libnss-winbind libpam-krb5 krb5-config krb5-user dnsutils chrony net-toolsDuring the Kerberos installation, you will be prompted to enter the chosen realm domain in uppercase letters, as initially defined: SVGENEBANK.LAN:
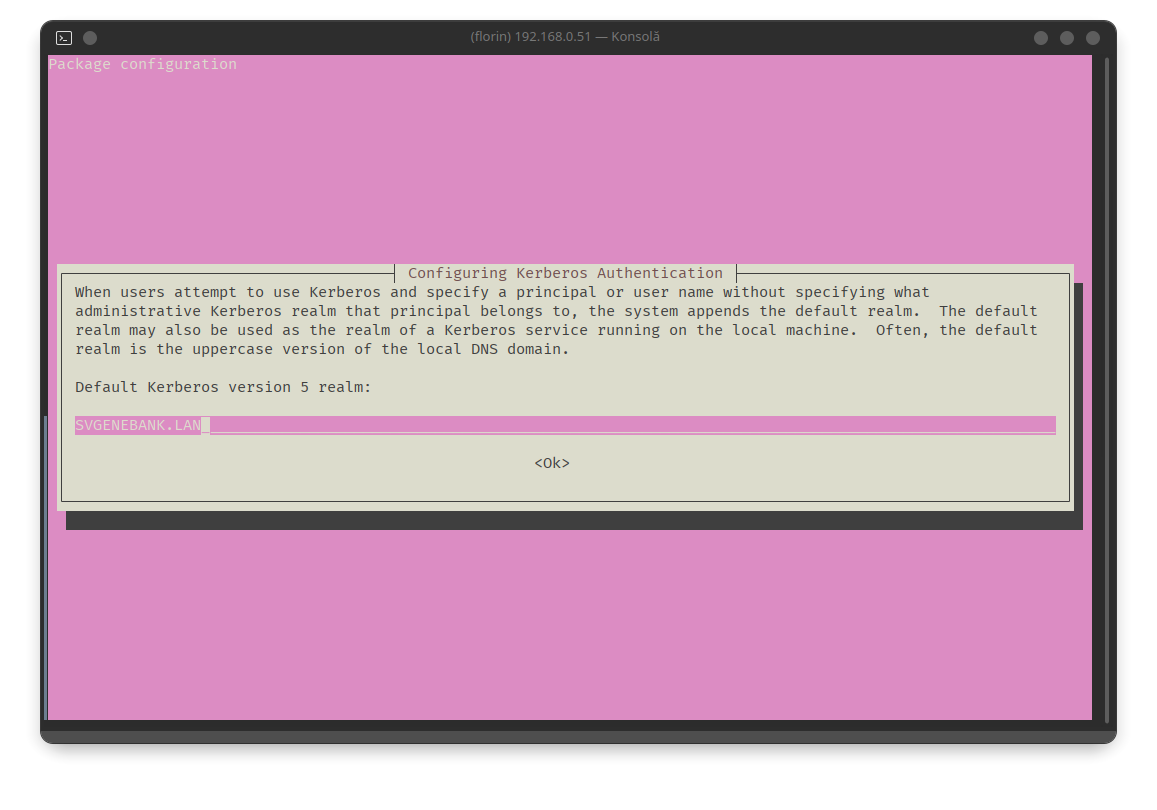 After entering the information and clicking
After entering the information and clicking
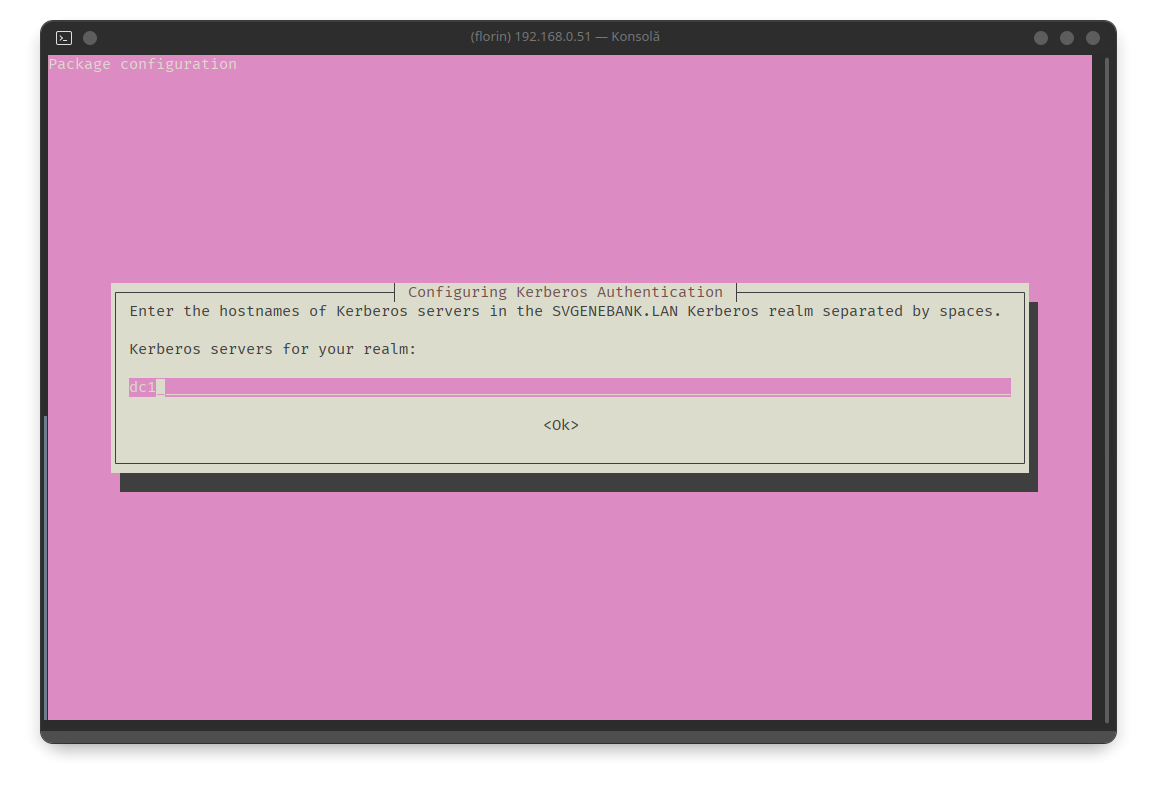
After entering the information and clicking
 Next, disable the unused Samba services and enable the AD-DC service:
Next, disable the unused Samba services and enable the AD-DC service:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl disable --now smbd nmbd winbind
Synchronizing state of smbd.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install disable smbd
Synchronizing state of nmbd.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install disable nmbd
Synchronizing state of winbind.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install disable winbind
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/winbind.service".
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/smbd.service".
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nmbd.service".
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/smb.service".
Removed "/etc/systemd/system/nmb.service".
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl unmask samba-ad-dc
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl enable samba-ad-dc
Synchronizing state of samba-ad-dc.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable samba-ad-dcSamba Server Configuration
Before modifying the configuration files, it is advisable to back them up; however, first stop the Samba AD-DC service:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl stop samba-ad-dc.service
florin@dc1:~$ sudo mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.orig
florin@dc1:~$ sudo mv /etc/krb5.conf /etc/krb5.conf.origFor interactive configuration, execute the following command:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 --interactive
Realm [SVGENEBANK.LAN]:
Domain [SVGENEBANK]:
Server Role (dc, member, standalone) [dc]:
DNS backend (SAMBA_INTERNAL, BIND9_FLATFILE, BIND9_DLZ, NONE) [SAMBA_INTERNAL]:
DNS forwarder IP address (write 'none' to disable forwarding) [192.168.0.51]: 8.8.8.8
Administrator password:
Retype password: The previous command generated the configuration file at /var/lib/samba/private/krb5.conf; this file must be copied to /etc/krb5.conf.
florin@dc1:~$ sudo cp /var/lib/samba/private/krb5.conf /etc/krb5.confNext, start the service and verify its status:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl start samba-ad-dc.service
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl status samba-ad-dc.service
● samba-ad-dc.service - Samba AD Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/samba-ad-dc.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-05-19 10:09:17 EEST; 10s ago
Docs: man:samba(8)
man:samba(7)
man:smb.conf(5)
Process: 3313 ExecCondition=/usr/share/samba/is-configured samba (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3316 (samba)
Status: "samba: ready to serve connections..."
Tasks: 58 (limit: 4609)
Memory: 176.2M (peak: 259.9M)
CPU: 1.619s
CGroup: /system.slice/samba-ad-dc.service
├─3316 "samba: root process"
├─3317 "samba: tfork waiter process(3318)"
├─3318 "samba: task[s3fs] pre-fork master"
├─3319 "samba: tfork waiter process(3320)"
├─3320 "samba: task[rpc] pre-fork master"
├─3321 "samba: tfork waiter process(3325)"
├─3322 "samba: tfork waiter process(3323)"
├─3323 "samba: task[nbt] pre-fork master"
├─3324 "samba: tfork waiter process(3327)"
├─3325 /usr/sbin/smbd -D "--option=server role check:inhibit=yes" --foreground
├─3326 "samba: tfork waiter process(3328)"
├─3327 "samba: task[wrepl] pre-fork master"
├─3328 "samba: task[rpc] pre-forked worker(0)"
├─3329 "samba: tfork waiter process(3332)"
├─3330 "samba: tfork waiter process(3331)"
├─3331 "samba: task[ldap] pre-fork master"
├─3332 "samba: task[rpc] pre-forked worker(1)"
├─3333 "samba: tfork waiter process(3334)"
├─3334 "samba: task[cldap] pre-fork master"
├─3335 "samba: tfork waiter process(3337)"
├─3336 "samba: tfork waiter process(3339)"
├─3337 "samba: task[rpc] pre-forked worker(2)"
├─3338 "samba: tfork waiter process(3341)"
├─3339 "samba: task[kdc] pre-fork master"
├─3340 "samba: tfork waiter process(3344)"
├─3341 "samba: task[rpc] pre-forked worker(3)"
├─3342 "samba: tfork waiter process(3343)"
├─3343 "samba: task[kdc] pre-forked worker(0)"
├─3344 "samba: task[drepl] pre-fork master"
├─3345 "samba: tfork waiter process(3347)"
├─3346 "samba: tfork waiter process(3348)"
├─3347 "samba: task[kdc] pre-forked worker(1)"
├─3348 "samba: task[winbindd] pre-fork master"
├─3349 "samba: tfork waiter process(3353)"
├─3350 "samba: tfork waiter process(3352)"
├─3351 "samba: tfork waiter process(3354)"
├─3352 "samba: task[ntp_signd] pre-fork master"
├─3353 "samba: task[kdc] pre-forked worker(2)"
├─3354 /usr/sbin/winbindd -D "--option=server role check:inhibit=yes" --foreground
├─3355 "samba: tfork waiter process(3357)"
├─3356 "samba: tfork waiter process(3358)"
├─3357 "samba: task[kcc] pre-fork master"
├─3358 "samba: task[kdc] pre-forked worker(3)"
├─3360 "samba: tfork waiter process(3361)"
├─3361 "samba: task[dnsupdate] pre-fork master"
├─3362 "samba: tfork waiter process(3363)"
├─3363 "samba: task[dns] pre-fork master"
├─3369 "smbd: notifyd" .
├─3370 "smbd: cleanupd "
├─3371 "winbindd: domain child [SVGENEBANK]"
├─3372 "samba: tfork waiter process(3373)"
├─3373 "samba: task[ldap] pre-forked worker(0)"
├─3374 "samba: tfork waiter process(3375)"
├─3375 "samba: task[ldap] pre-forked worker(1)"
├─3376 "samba: tfork waiter process(3377)"
├─3377 "samba: task[ldap] pre-forked worker(2)"
├─3378 "samba: tfork waiter process(3379)"
└─3379 "samba: task[ldap] pre-forked worker(3)"
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 samba[3331]: Attempting to autogenerate TLS self-signed keys for https for hostname 'DC1.svge>
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 smbd[3325]: [2025/05/19 10:09:17.514447, 0] source3/smbd/server.c:1746(main)
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 smbd[3325]: smbd version 4.19.5-Ubuntu started.
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 smbd[3325]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2023
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 systemd[1]: Started samba-ad-dc.service - Samba AD Daemon.
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 winbindd[3354]: [2025/05/19 10:09:17.581196, 0] source3/winbindd/winbindd.c:1441(main)
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 winbindd[3354]: winbindd version 4.19.5-Ubuntu started.
May 19 10:09:17 dc1 winbindd[3354]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2023
May 19 10:09:18 dc1 samba[3331]: [2025/05/19 10:09:18.068290, 0] source4/lib/tls/tlscert.c:154(tls_cert_generate)
May 19 10:09:18 dc1 samba[3331]: TLS self-signed keys generated OKCreating the reverse DNS zone
At this point, the DNS reverse zone can be created. Install the package that provides the setproctitle module for Python:
florin@dc1:~$ samba-tool dns zonecreate dc1.svgenebank.lan 0.168.192.in-addr.arpa -U Administrator
WARNING: Using passwords on command line is insecure. Installing the setproctitle python module will hide these from shortly after program start.
Password for [SVGENEBANK\Administrator]:
Zone 0.168.192.in-addr.arpa created successfully
florin@dc1:~$ sudo apt install python3-setproctitle
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool dns add dc1.svgenebank.lan 0.168.192.in-addr.arpa 1 PTR dc1.svgenebank.lan -U Administrator
Password for [SVGENEBANK\Administrator]:
Record added successfullyService testing
Testing anonymous connection and authentication:
florin@dc1:~$ smbclient -L localhost -N
Anonymous login successful
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
sysvol Disk
netlogon Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.19.5-Ubuntu)
SMB1 disabled -- no workgroup available
florin@dc1:~$ smbclient //localhost/netlogon -UAdministrator -c 'ls'
Password for [SVGENEBANK\Administrator]:
. D 0 Mon May 19 10:06:46 2025
.. D 0 Mon May 19 10:06:46 2025
11758760 blocks of size 1024. 6040504 blocks availableTesting DNS resolution for domain records:
florin@dc1:~$ host -t A dc1.svgenbank.lan
dc1.svgenbank.lan has no A record
florin@dc1:~$ host -t A dc1.svgenebank.lan
dc1.svgenebank.lan has address 192.168.0.51
florin@dc1:~$ host -t SRV _ldap._tcp.svgenebank.lan
_ldap._tcp.svgenebank.lan has SRV record 0 100 389 dc1.svgenebank.lan.
florin@dc1:~$ host -t SRV _kerberos._udp.svgenebank.lan
_kerberos._udp.svgenebank.lan has SRV record 0 100 88 dc1.svgenebank.lan.Kerberos testing
florin@dc1:~$ kinit administrator
Password for administrator@SVGENEBANK.LAN:
Warning: Your password will expire in 41 days on Mon Jun 30 10:06:49 2025
florin@dc1:~$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000
Default principal: administrator@SVGENEBANK.LAN
Valid starting Expires Service principal
05/19/25 10:19:50 05/19/25 20:19:50 krbtgt/SVGENEBANK.LAN@SVGENEBANK.LAN
renew until 05/20/25 10:19:42Listing users and groups
florin@dc1:~$ wbinfo -u
SVGENEBANK\administrator
SVGENEBANK\guest
SVGENEBANK\krbtgt
florin@dc1:~$ wbinfo -g
SVGENEBANK\cert publishers
SVGENEBANK\ras and ias servers
SVGENEBANK\allowed rodc password replication group
SVGENEBANK\denied rodc password replication group
SVGENEBANK\dnsadmins
SVGENEBANK\enterprise read-only domain controllers
SVGENEBANK\domain admins
SVGENEBANK\domain users
SVGENEBANK\domain guests
SVGENEBANK\domain computers
SVGENEBANK\domain controllers
SVGENEBANK\schema admins
SVGENEBANK\enterprise admins
SVGENEBANK\group policy creator owners
SVGENEBANK\read-only domain controllers
SVGENEBANK\protected users
SVGENEBANK\dnsupdateproxyConfiguring the Active Directory time synchronization service
The chronyd service was utilized for synchronization.
First, change the ownership of the directory /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo ls -ld /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
drwxr-x--- 2 root root 4096 May 19 10:16 /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
florin@dc1:~$ sudo chown root:_chrony /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
florin@dc1:~$ sudo ls -ld /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
drwxr-x--- 2 root _chrony 4096 May 19 10:16 /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
florin@dc1:~$ sudo chmod 750 /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
florin@dc1:~$ sudo ls -ld /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
drwxr-x--- 2 root _chrony 4096 May 19 10:16 /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/Next, edit the configuration file /etc/chrony/chrony.conf for the chronyd service:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo nano /etc/chrony/chrony.confAdd the following lines:
# IP address of this DC
bindcmdaddress 192.168.0.51
# DNS netmask
allow 192.168.0.0/24
ntpsigndsocket /var/lib/samba/ntp_signdThe file will then appear as follows:
# Welcome to the chrony configuration file. See chrony.conf(5) for more
# information about usable directives.
# Include configuration files found in /etc/chrony/conf.d.
confdir /etc/chrony/conf.d
# This will use (up to):
# - 4 sources from ntp.ubuntu.com, some of which are IPv6 enabled
# - 2 sources from 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org, which is also IPv6 enabled
# - 1 source from [01].ubuntu.pool.ntp.org each (IPv4 only at the moment)
# This means that by default, up to 6 dual-stack and up to 2 additional IPv4-only
# sources will be used.
# At the same time, it retains some protection against one of the entries being
# down (compared to using just one of the lines). See (LP: #1754358) for the
# discussion.
#
# For information about using servers from the NTP Pool Project in general, see (LP: #104525).
# Approved by the Ubuntu Technical Board on 2011-02-08.
# See http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html for more information.
pool ntp.ubuntu.com iburst maxsources 4
pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst maxsources 1
pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst maxsources 1
pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst maxsources 2
# Use time sources provided by DHCP.
sourcedir /run/chrony-dhcp
# Use NTP sources found in /etc/chrony/sources.d.
sourcedir /etc/chrony/sources.d
# This directive specifies the location of the file containing ID/key pairs for
# NTP authentication.
keyfile /etc/chrony/chrony.keys
# This directive specifies the file into which chronyd will store the rate
# information.
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
# Save NTS keys and cookies.
ntsdumpdir /var/lib/chrony
# Uncomment the following line to enable logging.
# Log tracking, measurements, and statistics
# Location of log files.
logdir /var/log/chrony
# Prevent inaccurate estimates from disrupting the machine clock.
maxupdateskew 100.0
# This directive enables kernel synchronization (every 11 minutes) of the
# real-time clock. Note that this cannot be used together with the 'rtcfile' directive.
rtcsync
# Step the system clock instead of slewing it if the adjustment exceeds
# one second, but only during the first three clock updates.
makestep 1 3
# Retrieve TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system timezone database.
# This directive must be commented out when using time sources that provide
# leap-smeared time.
leapsectz right/UTC
# IP address of this DC
bindcmdaddress 192.168.0.51
# DNS netmask
allow 192.168.0.0/24
ntpsigndsocket /var/lib/samba/ntp_signdAfter editing and saving, restart the service:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl restart chronydVerify that it is functioning correctly:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl status chronyd
● chrony.service - chrony, an NTP client/server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/chrony.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-05-19 10:42:56 EEST; 9s ago
Docs: man:chronyd(8)
man:chronyc(1)
man:chrony.conf(5)
Process: 1381 ExecStart=/usr/lib/systemd/scripts/chronyd-starter.sh $DAEMON_OPTS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 1392 (chronyd)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4609)
Memory: 1.4M (peak: 2.2M)
CPU: 36ms
CGroup: /system.slice/chrony.service
├─1392 /usr/sbin/chronyd -F 1
└─1393 /usr/sbin/chronyd -F 1
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 systemd[1]: Starting chrony.service - chrony, an NTP client/server...
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 chronyd[1392]: chronyd version 4.5 starting (+CMDMON +NTP +REFCLOCK +RTC +PRIVDROP +SCFILTER +S>
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 chronyd[1392]: Loaded 0 symmetric keys
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 chronyd[1392]: Frequency -3.984 +/- 0.106 ppm read from /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 chronyd[1392]: Using right/UTC timezone to obtain leap second data
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 chronyd[1392]: MS-SNTP authentication enabled
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 chronyd[1392]: Loaded seccomp filter (level 1)
May 19 10:42:56 dc1 systemd[1]: Started chrony.service - chrony, an NTP client/server.
May 19 10:43:02 dc1 chronyd[1392]: Selected source 185.125.190.57 (ntp.ubuntu.com)
May 19 10:43:02 dc1 chronyd[1392]: System clock TAI offset set to 37 seconds
florin@dc1:~$ chronyc sources
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^+ prod-ntp-3.ntp1.ps5.cano> 2 6 17 29 -2246us[-2841us] +/- 28ms
^* prod-ntp-4.ntp1.ps5.cano> 2 6 17 28 -2185us[-2780us] +/- 28ms
^+ prod-ntp-5.ntp4.ps5.cano> 2 6 17 28 -700us[-1295us] +/- 30ms
^+ alphyn.canonical.com 2 6 17 29 +646us[ +51us] +/- 84ms
^+ time.cloudflare.com 3 6 17 28 +3304us[+2709us] +/- 31ms
^- time5.hamcloud.ro 3 6 17 29 +16ms[ +15ms] +/- 74ms
^+ ntp3.hamcloud.ro 3 6 17 28 +8845us[+8250us] +/- 70ms
^- time8.hamcloud.ro 3 6 17 29 +5642us[+5047us] +/- 56ms
florin@dc1:~$ chronyc tracking
Reference ID : B97DBE39 (prod-ntp-4.ntp4.ps5.canonical.com)
Stratum : 3
Ref time (UTC) : Mon May 19 07:43:04 2025
System time : 0.000000049 seconds fast of NTP time
Last offset : -0.000595212 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000595212 seconds
Frequency : 3.984 ppm slow
Residual freq : +13.368 ppm
Skew : 0.106 ppm
Root delay : 0.055841085 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.001371672 seconds
Update interval : 2.0 seconds
Leap status : Normal
florin@dc1:~$ timedatectl
Local time: Mon 2025-05-19 10:45:13 EEST
Universal time: Mon 2025-05-19 07:45:13 UTC
RTC time: Mon 2025-05-19 07:45:13
Time zone: Europe/Bucharest (EEST, +0300)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: active
RTC in local TZ: noUser and group management
For users
Adding a user
To add a new user, execute the command samba-tool user add. To begin, request the command's help to view the parameters that can be used with this command:
florin@dc1:~$ samba-tool user add -h
Usage: samba-tool user add <username> [<password>] [options]
Add a new user.
This command adds a new user account to the Active Directory domain. The
username specified on the command is the sAMaccountName.
User accounts may represent physical entities, such as people or may be used
as service accounts for applications. User accounts are also referred to as
security principals and are assigned a security identifier (SID).
A user account enables a user to logon to a computer and domain with an
identity that can be authenticated. To maximize security, each user should
have their own unique user account and password. A user's access to domain
resources is based on permissions assigned to the user account.
Unix (RFC2307) attributes may be added to the user account. Attributes taken
from NSS are obtained on the local machine. Explicitly given values override
values obtained from NSS. Configure 'idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = Yes' to use these
attributes for UID/GID mapping.
The command may be run from the root userid or another authorized userid. The
-H or --URL= option can be used to execute the command against a remote
server.
Example1:
samba-tool user add User1 passw0rd --given-name=John --surname=Smith --must-
change-at-next-login -H ldap://samba.samdom.example.com
-Uadministrator%passw1rd
Example1 shows how to add a new user to the domain against a remote LDAP
server. The -H parameter is used to specify the remote target server. The -U
option is used to pass the userid and password authorized to issue the command
remotely.
Example2:
sudo samba-tool user add User2 passw2rd --given-name=Jane --surname=Doe
--must-change-at-next-login
Example2 shows how to add a new user to the domain against the local server.
sudo is used so a user may run the command as root. In this example, after
User2 is created, he/she will be forced to change their password when they
logon.
Example3:
samba-tool user add User3 passw3rd --userou='OU=OrgUnit'
Example3 shows how to add a new user in the OrgUnit organizational unit.
Example4:
samba-tool user add User4 passw4rd --rfc2307-from-nss --gecos 'some text'
Example4 shows how to add a new user with Unix UID, GID and login-shell set
from the local NSS and GECOS set to 'some text'.
Example5:
samba-tool user add User5 passw5rd --nis-domain=samdom --unix-home=/home/User5
\
--uid-number=10005 --login-shell=/bin/false --gid-number=10000
Example5 shows how to add a new RFC2307/NIS domain enabled user account. If
--nis-domain is set, then the other four parameters are mandatory.
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-H URL, --URL=URL LDB URL for database or target server
--must-change-at-next-login
Force password to be changed on next login
--random-password Generate random password
--smartcard-required Require a smartcard for interactive logons
--use-username-as-cn Force use of username as user's CN
--userou=USEROU DN of alternative location (without domainDN
counterpart) to default CN=Users in which new user
object will be created. E. g. 'OU=<OU name>'
--surname=SURNAME User's surname
--given-name=GIVEN_NAME
User's given name
--initials=INITIALS User's initials
--profile-path=PROFILE_PATH
User's profile path
--script-path=SCRIPT_PATH
User's logon script path
--home-drive=HOME_DRIVE
User's home drive letter
--home-directory=HOME_DIRECTORY
User's home directory path
--job-title=JOB_TITLE
User's job title
--department=DEPARTMENT
User's department
--company=COMPANY User's company
--description=DESCRIPTION
User's description
--mail-address=MAIL_ADDRESS
User's email address
--internet-address=INTERNET_ADDRESS
User's home page
--telephone-number=TELEPHONE_NUMBER
User's phone number
--physical-delivery-office=PHYSICAL_DELIVERY_OFFICE
User's office location
--rfc2307-from-nss Copy Unix user attributes from NSS (will be overridden
by explicit UID/GID/GECOS/shell)
--nis-domain=NIS_DOMAIN
User's Unix/RFC2307 NIS domain
--unix-home=UNIX_HOME
User's Unix/RFC2307 home directory
--uid=UID User's Unix/RFC2307 username
--uid-number=UID_NUMBER
User's Unix/RFC2307 numeric UID
--gid-number=GID_NUMBER
User's Unix/RFC2307 primary GID number
--gecos=GECOS User's Unix/RFC2307 GECOS field
--login-shell=LOGIN_SHELL
User's Unix/RFC2307 login shell
--color=always|never|auto
use colour if available (default: auto)
Credentials Options:
--simple-bind-dn=DN
DN to use for a simple bind
--password=PASSWORD
Password
-U USERNAME, --username=USERNAME
Username
-W WORKGROUP, --workgroup=WORKGROUP
Workgroup
-N, --no-pass Don't ask for a password
--ipaddress=IPADDRESS
IP address of server
-P, --machine-pass Use stored machine account password
--use-kerberos=desired|required|off
Use Kerberos authentication
--use-krb5-ccache=KRB5CCNAME
Kerberos Credentials cache
-A AUTHFILE, --authentication-file=AUTHFILE
Authentication file
-k KERBEROS, --kerberos=KERBEROS
DEPRECATED: Migrate to --use-kerberos
Samba Common Options:
-s FILE, --configfile=FILE
Configuration file
-d DEBUGLEVEL, --debuglevel=DEBUGLEVEL
debug level
--option=OPTION set smb.conf option from command line
--realm=REALM set the realm name
Version Options:
-V, --version Display version numberAn example of adding a user on a local server (use the -H parameter for remote servers):
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user add florint --given-name=Florin --surname=Tanasă --initials=FT --mail-address=florin.tanasa@genebanksv.ro --job-title='Specialist engineer' --department='IT&IC' --company='Genebank Suceava'--internet-address=genebanksv.ro --login-shell=/bin/bash
[sudo] password for florin:
New Password:
Retype Password:
User 'florint' added successfullyListing users:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user list
krbtgt
Guest
florint
AdministratorDeleting a user:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user delete user_name_domainChanging a user's password:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user setpassword user_name_domainDisabling and enabling a user:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user disable user_name_domain
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user enable user_name_domainFor groups:
Adding a group:
To add a new group, use the command samba-tool group add. To begin, request the command's help to view the parameters that can be used with this command:
florin@dc1:~$ samba-tool group -h add
Usage: samba-tool group add <groupname> [options]
Creates a new AD group.
This command adds a new Active Directory group. The groupname specified on
the command is a unique sAMAccountName.
An Active Directory group may contain user and computer accounts as well as
other groups. An administrator adds a new group and adds members to that
group so they can be managed as a single entity. This helps to simplify
security and system administration.
Groups may also be used to establish email distribution lists, using --group-
type=Distribution.
Groups are located in domains in organizational units (OUs). The group's
scope is a characteristic of the group that designates the extent to which the
group is applied within the domain tree or forest.
The group location (OU), type (security or distribution) and scope may all be
specified on the samba-tool command when the group is created.
The command may be run from the root userid or another authorized userid. The
-H or --URL= option can be used to execute the command on a remote server.
Example1:
samba-tool group add Group1 -H ldap://samba.samdom.example.com
--description='Simple group'
Example1 adds a new group with the name Group1 added to the Users container on
a remote LDAP server. The -U parameter is used to pass the userid and
password of a user that exists on the remote server and is authorized to issue
the command on that server. It defaults to the security type and global
scope.
Example2:
sudo samba-tool group add Group2 --group-type=Distribution
Example2 adds a new distribution group to the local server. The command is
run under root using the sudo command.
Example3:
samba-tool group add Group3 --nis-domain=samdom --gid-number=12345
Example3 adds a new RFC2307 enabled group for NIS domain samdom and GID 12345
(both options are required to enable this feature).
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-H URL, --URL=URL LDB URL for database or target server
--groupou=GROUPOU Alternative location (without domainDN counterpart) to
default CN=Users in which new user object will be
created
--group-scope=GROUP_SCOPE
Group scope (Domain | Global | Universal)
--group-type=GROUP_TYPE
Group type (Security | Distribution)
--description=DESCRIPTION
Group's description
--mail-address=MAIL_ADDRESS
Group's email address
--notes=NOTES Groups's notes
--gid-number=GID_NUMBER
Group's Unix/RFC2307 GID number
--nis-domain=NIS_DOMAIN
SFU30 NIS Domain
--special Add a special predefined group
--color=always|never|auto
use colour if available (default: auto)
Credentials Options:
--simple-bind-dn=DN
DN to use for a simple bind
--password=PASSWORD
Password
-U USERNAME, --username=USERNAME
Username
-W WORKGROUP, --workgroup=WORKGROUP
Workgroup
-N, --no-pass Don't ask for a password
--ipaddress=IPADDRESS
IP address of server
-P, --machine-pass Use stored machine account password
--use-kerberos=desired|required|off
Use Kerberos authentication
--use-krb5-ccache=KRB5CCNAME
Kerberos Credentials cache
-A AUTHFILE, --authentication-file=AUTHFILE
Authentication file
-k KERBEROS, --kerberos=KERBEROS
DEPRECATED: Migrate to --use-kerberos
Samba Common Options:
-s FILE, --configfile=FILE
Configuration file
-d DEBUGLEVEL, --debuglevel=DEBUGLEVEL
debug level
--option=OPTION set smb.conf option from command line
--realm=REALM set the realm name
Version Options:
-V, --version Display version numberFor demonstration, a group named IT-IC will be created:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group add IT-IC --description='Group for IT and IC members' --mail-address=it.ic@genebanksv.ro
Added group IT-ICDeleting a group:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group delete group_nameListing groups:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group list
Incoming Forest Trust Builders
Distributed COM Users
Domain Guests
Terminal Server License Servers
Domain Admins
Windows Authorization Access Group
Network Configuration Operators
Account Operators
Domain Users
Domain Controllers
Server Operators
Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access
Guests
Read-only Domain Controllers
Print Operators
RAS and IAS Servers
Performance Monitor Users
Group Policy Creator Owners
DnsUpdateProxy
Domain Computers
Cert Publishers
Performance Log Users
Event Log Readers
Cryptographic Operators
Schema Admins
IT-IC
Certificate Service DCOM Access
Enterprise Admins
DnsAdmins
Denied RODC Password Replication Group
Protected Users
IIS_IUSRS
Replicator
Users
Remote Desktop Users
Allowed RODC Password Replication Group
Administrators
Enterprise Read-only Domain Controllers
Backup OperatorsListing users who are members of a group:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group listmembers "Domain Users"
Administrator
krbtgt
florint
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group listmembers "Domain Admins"
AdministratorAdding new members to a group:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group addmembers IT-IC florint
Added members to group IT-ICRemoving members from a group
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group removemembers IT-IC florint
Removed members from group IT-ICInformation on the domain password policy
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool domain passwordsettings show
Password information for domain 'DC=svgenebank,DC=lan'
Password complexity: on
Store plaintext passwords: off
Password history length: 24
Minimum password length: 7
Minimum password age (days): 1
Maximum password age (days): 42
Account lockout duration (mins): 30
Account lockout threshold (attempts): 0
Reset account lockout after (mins): 30Local authentication on the AD-DC server using AD accounts
By default, AD users cannot log into the dc1 system using AD accounts created with samba-tool. To enable authentication, it is necessary to configure the PAM controller that allows system access.
First, we will make several modifications to the smb.conf configuration file of the samba service:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.confIn the [global] section, we will add the following directives:
winbind enum users = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
template shell = /bin/bash
template homedir = /home/%UThe file will have the following structure:
# Global parameters
[global]
dns forwarder = 8.8.8.8
netbios name = DC1
realm = SVGENEBANK.LAN
server role = active directory domain controller
workgroup = SVGENEBANK
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
winbind enum users = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
template shell = /bin/bash
template homedir = /home/%U
[sysvol]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol
read only = No
[netlogon]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/svgenebank.lan/scripts
read only = NoVerify the configuration file for errors using the testparm command, and if no errors are found, restart the service:
florin@dc1:~$ testparm
Load smb config files from /etc/samba/smb.conf
Loaded services file OK.
Weak crypto is allowed by GnuTLS (e.g. NTLM as a compatibility fallback)
Server role: ROLE_ACTIVE_DIRECTORY_DC
Press enter to see a dump of your service definitions
# Global parameters
[global]
dns forwarder = 8.8.8.8
passdb backend = samba_dsdb
realm = SVGENEBANK.LAN
server role = active directory domain controller
template homedir = /home/%U
template shell = /bin/bash
winbind enum groups = Yes
winbind enum users = Yes
workgroup = SVGENEBANK
rpc_server:tcpip = no
rpc_daemon:spoolssd = embedded
rpc_server:spoolss = embedded
rpc_server:winreg = embedded
rpc_server:ntsvcs = embedded
rpc_server:eventlog = embedded
rpc_server:srvsvc = embedded
rpc_server:svcctl = embedded
rpc_server:default = external
winbindd:use external pipes = true
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
idmap config * : backend = tdb
map archive = No
vfs objects = dfs_samba4 acl_xattr
[sysvol]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol
read only = No
[netlogon]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/svgenebank.lan/scripts
read only = No
florin@dc1:~$ sudo systemctl restart samba-ad-dc.serviceTo query Active Directory, several applications such as getent and wbinfo can be used:
florin@dc1:~$ getent passwd | grep SVGENEBANK
SVGENEBANK\administrator:*:0:100::/home/administrator:/bin/bash
SVGENEBANK\guest:*:3000011:3000012::/home/guest:/bin/bash
SVGENEBANK\krbtgt:*:3000018:100::/home/krbtgt:/bin/bash
SVGENEBANK\florint:*:3000017:100::/home/florint:/bin/bash
florin@dc1:~$ getent group | grep SVGENEBANK
SVGENEBANK\cert publishers:x:3000035:
SVGENEBANK\ras and ias servers:x:3000036:
SVGENEBANK\allowed rodc password replication group:x:3000037:
SVGENEBANK\denied rodc password replication group:x:3000005:
SVGENEBANK\dnsadmins:x:3000038:
SVGENEBANK\enterprise read-only domain controllers:x:3000039:
SVGENEBANK\domain admins:x:3000004:
SVGENEBANK\domain users:x:100:
SVGENEBANK\domain guests:x:3000012:
SVGENEBANK\domain computers:x:3000040:
SVGENEBANK\domain controllers:x:3000041:
SVGENEBANK\schema admins:x:3000006:
SVGENEBANK\enterprise admins:x:3000007:
SVGENEBANK\group policy creator owners:x:3000008:
SVGENEBANK\read-only domain controllers:x:3000042:
SVGENEBANK\protected users:x:3000043:
SVGENEBANK\dnsupdateproxy:x:3000044:
SVGENEBANK\it-ic:x:3000045:
florin@dc1:~$ wbinfo -u
SVGENEBANK\administrator
SVGENEBANK\guest
SVGENEBANK\krbtgt
SVGENEBANK\florint
florin@dc1:~$ wbinfo -g
SVGENEBANK\cert publishers
SVGENEBANK\ras and ias servers
SVGENEBANK\allowed rodc password replication group
SVGENEBANK\denied rodc password replication group
SVGENEBANK\dnsadmins
SVGENEBANK\enterprise read-only domain controllers
SVGENEBANK\domain admins
SVGENEBANK\domain users
SVGENEBANK\domain guests
SVGENEBANK\domain computers
SVGENEBANK\domain controllers
SVGENEBANK\schema admins
SVGENEBANK\enterprise admins
SVGENEBANK\group policy creator owners
SVGENEBANK\read-only domain controllers
SVGENEBANK\protected users
SVGENEBANK\dnsupdateproxy
SVGENEBANK\it-ic
florin@dc1:~$ wbinfo -i florint
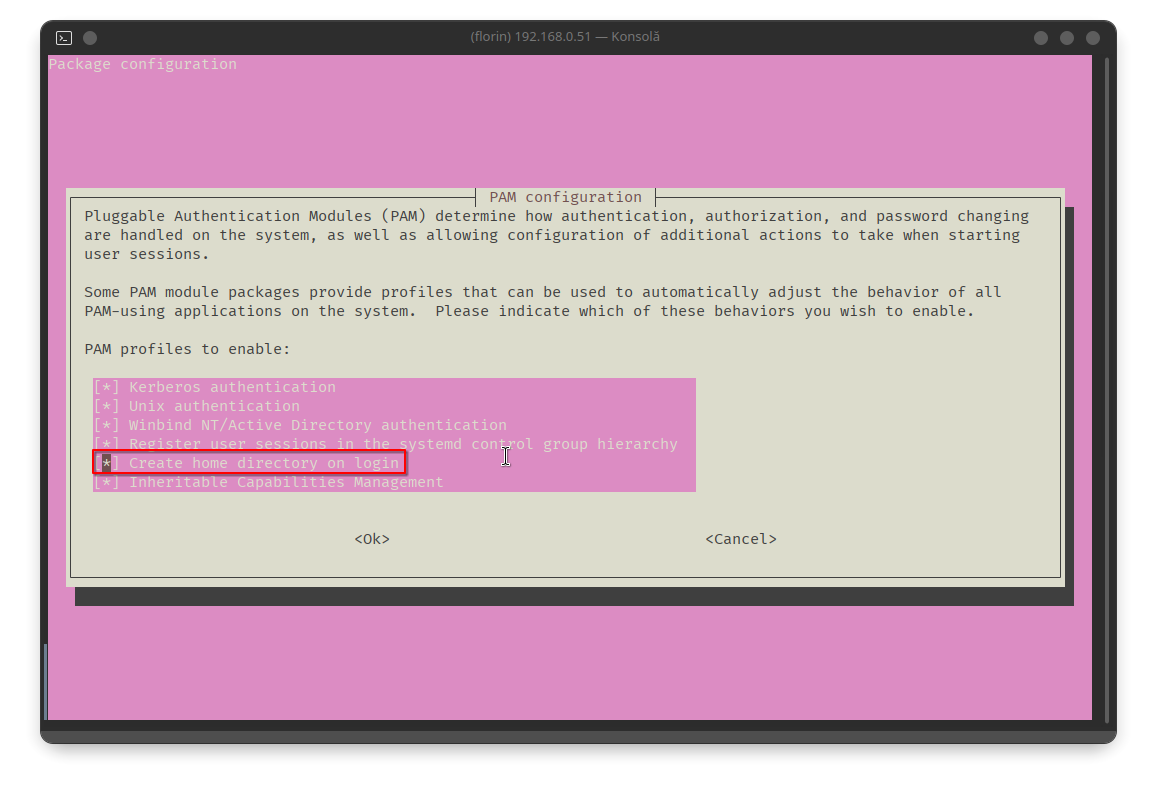
SVGENEBANK\florint:*:3000017:100::/home/florint:/bin/bashNext, modifications will be applied to the PAM (Linux Pluggable Authentication Modules) configuration files. Ubuntu provides a utility for this purpose:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo pam-auth-update We will configure the system to automatically create the home directory upon user login:
 For testing, we will log in with a domain user:
For testing, we will log in with a domain user:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo su - florint
Creating directory '/home/florint'.
SVGENEBANK\florint@dc1:~$ ls -a
. .. .bash_logout .bashrc .profile
SVGENEBANK\florint@dc1:~$ whoami
SVGENEBANK\florint
florin@dc1:~$ su - florint
Password:
groups: cannot find name for group ID 3000046
SVGENEBANK\florint@dc1:~$ whoami
SVGENEBANK\florint
SVGENEBANK\florint@dc1:~$ id
uid=3000017(SVGENEBANK\florint) gid=100(users) groups=100(users),3000009(BUILTIN\users),3000017(SVGENEBANK\florint),3000045(SVGENEBANK\it-ic),3000046There is a group ID without a name, most likely originating from one created and deleted during testing.
Domain users can now log in locally to the server.
For remote connections via ssh:
florin@dc1:~$ ssh florint@dc1.svgenebank.lan
florint@dc1.svgenebank.lan's password:
Warning: Your password will expire in 41 days on Mon Jun 30 14:17:25 2025
Warning: Your password will expire in 41 days on Mon Jun 30 14:17:25 2025
Welcome to Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 6.8.0-60-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/pro
System information as of Tue May 20 10:17:41 AM EEST 2025
System load: 0.0 Processes: 203
Usage of /: 43.8% of 11.21GB Users logged in: 2
Memory usage: 11% IPv4 address for enp1s0: 192.168.0.51
Swap usage: 0%
* Strictly confined Kubernetes makes edge and IoT secure. Learn how MicroK8s
just raised the bar for easy, resilient and secure K8s cluster deployment.
https://ubuntu.com/engage/secure-kubernetes-at-the-edge
Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled.
0 updates can be applied immediately.
Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates.
See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status
Last login: Tue May 20 10:15:30 2025 from 192.168.0.51
groups: cannot find name for group ID 3000046Authentication via ssh using a domain user's username and password also functions correctly.
Enrolling a Linux client into the AD-DC
It is crucial that the devices to be added have their clocks synchronized with the server, in this case dc1.svgenebank.lan. Additionally, it is essential that the client device can resolve DNS queries for 'dc1.svgenebank.lan'; this can be achieved by editing /etc/resolv.conf.
Enrolling a device running Rocky Linux2
Configure the network interface with a static IP and define DNS resolution using the nmtui utility, which operates effectively in the console:
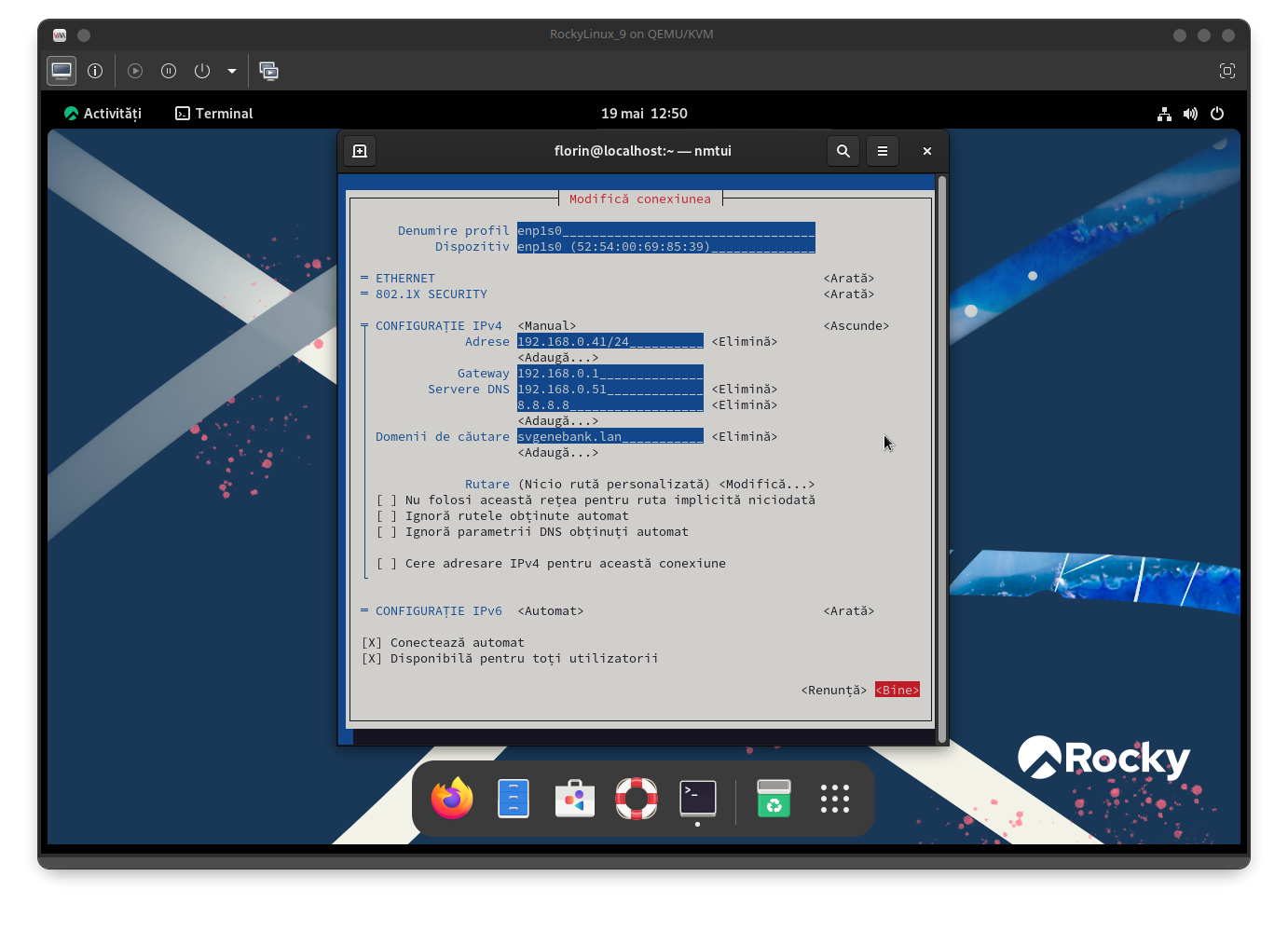 Set the client machine's hostname:
Set the client machine's hostname:
[florin@localhost ~]$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname florin-rockyDefine the machine in /etc/hosts as follows:
[florin@localhost ~]$ cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.0.41 florin-rocky.svgenebank.lan florin-rockyRestart the machine. After reboot, verify the following:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ ping -c3 google.ro
PING google.ro (172.217.169.99) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from sof02s31-in-f3.1e100.net (172.217.169.99): icmp_seq=1 ttl=112 time=25.7 ms
64 bytes from sof02s31-in-f3.1e100.net (172.217.169.99): icmp_seq=2 ttl=112 time=25.9 ms
64 bytes from sof02s31-in-f3.1e100.net (172.217.169.99): icmp_seq=3 ttl=112 time=25.8 ms
--- google.ro ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 25.745/25.797/25.852/0.043 ms
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ ping -c3 dc1
PING dc1.svgenebank.lan (192.168.0.51) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.51 (192.168.0.51): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.521 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.51 (192.168.0.51): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.781 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.51 (192.168.0.51): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.715 ms
--- dc1.svgenebank.lan ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.521/0.672/0.781/0.110 msTo synchronize the clock of the machine florin-rocky with the AD-DC server dc1, edit the configuration file of the chronyd service as follows:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo nano /etc/chrony.conf Apply the following modifications:
#pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Server from which the time is obtained
server 192.168.0.51 iburst
# IP address of this Unix domain member
bindcmdaddress 192.168.0.41The final chrony.conf file should appear as follows:
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (https://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Server from which the time is obtained
server 192.168.0.51 iburst
# IP address of this Unix domain member
bindcmdaddress 192.168.0.41
# Use NTP servers provided by DHCP.
sourcedir /run/chrony-dhcp
# Record the rate at which the system clock gains or loses time.
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift
# Allow the system clock to be stepped during the first three updates.
# If its offset exceeds 1 second.
makestep 1.0 3
# Enable kernel synchronization of the real-time clock (RTC).
rtcsync
# Enable hardware timestamping on all interfaces that support it.
#hwtimestamp *
# Increase the minimum number of selectable sources required to adjust
# the system clock.
#minsources 2
# Allow NTP client access from the local network.
#allow 192.168.0.0/16
# Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source.
#local stratum 10
# Require authentication (NTS or key option) for all NTP sources.
#authselectmode require
# Specify the file containing keys for NTP authentication.
keyfile /etc/chrony.keys
# Save NTS keys and cookies.
ntsdumpdir /var/lib/chrony
# Insert or delete leap seconds by slewing instead of stepping.
#leapsecmode slew
# Retrieve TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system timezone database.
leapsectz right/UTC
# Specify the directory for log files.
logdir /var/log/chrony
# Select which information is logged.
#log measurements statistics trackingAfter saving the chronyd service configuration file, the service will be restarted and its proper operation verified:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo systemctl restart chronyd
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo systemctl status chronyd
● chronyd.service - NTP client/server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/chronyd.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-05-19 13:02:55 EEST; 2s ago
Docs: man:chronyd(8)
man:chrony.conf(5)
Process: 2974 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/chronyd $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 2976 (chronyd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 16182)
Memory: 920.0K
CPU: 25ms
CGroup: /system.slice/chronyd.service
└─2976 /usr/sbin/chronyd -F 2
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky systemd[1]: Starting NTP client/server...
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky chronyd[2976]: chronyd version 4.5 starting (+CMDMON +NTP +REFCLOCK +RTC +PRIVDROP +SCFILTER +SIGND +ASYNCDNS +NTS +SECHASH +IPV>
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky chronyd[2976]: Loaded 0 symmetric keys
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky chronyd[2976]: Using right/UTC timezone to obtain leap second data
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky chronyd[2976]: Frequency -4.175 +/- 2.816 ppm read from /var/lib/chrony/drift
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky chronyd[2976]: Loaded seccomp filter (level 2)
mai 19 13:02:55 florin-rocky systemd[1]: Started NTP client/server.
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ chronyc sources
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^* 192.168.0.51 3 6 17 47 +11us[ +32us] +/- 29ms
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ chronyc tracking
Reference ID : C0A80033 (192.168.0.51)
Stratum : 4
Ref time (UTC) : Mon May 19 10:03:01 2025
System time : 0.000000004 seconds slow of NTP time
Last offset : +0.000021484 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000021484 seconds
Frequency : 4.175 ppm slow
Residual freq : +1.455 ppm
Skew : 2.929 ppm
Root delay : 0.055686146 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.001265819 seconds
Update interval : 2.0 seconds
Leap status : NormalAs observed, the clock of the machine florin-rocky is now synchronized with the clock of the AD-DC server dc1 (IP 192.168.0.51).
Next, install the packages containing the necessary applications to enroll the machine florin-rocky into the domain:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo dnf install realmd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir sssd adcli krb5-workstationVerify whether the domain server is visible:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ realm discover svgenebank.lan
svgenebank.lan
type: kerberos
realm-name: SVGENEBANK.LAN
domain-name: svgenebank.lan
configured: no
server-software: active-directory
client-software: sssd
required-package: oddjob
required-package: oddjob-mkhomedir
required-package: sssd
required-package: adcli
required-package: samba-common-toolsNext, enroll the machine running Rocky Linux:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo realm join dc1.svgenebank.lan
Password for Administrator@SVGENEBANK.LAN:
Warning: Your password will expire in 41 days on Lu 30 iun 2025 10:06:49 +0300After entering the domain administrator password, the machine florin-rocky will be enrolled in the domain svgenebank.lan.
Verification
After completing the above configurations, you can request information related to passwd to confirm proper operation:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo getent passwd administrator@svgenebank.lan
administrator@svgenebank.lan:*:487200500:487200513:Administrator:/home/administrator@svgenebank.lan:/bin/bashAs observed, our machine receives information from the Samba AD-DC server dc1.
Authentication using the username and password of a domain user in Rocky Linux
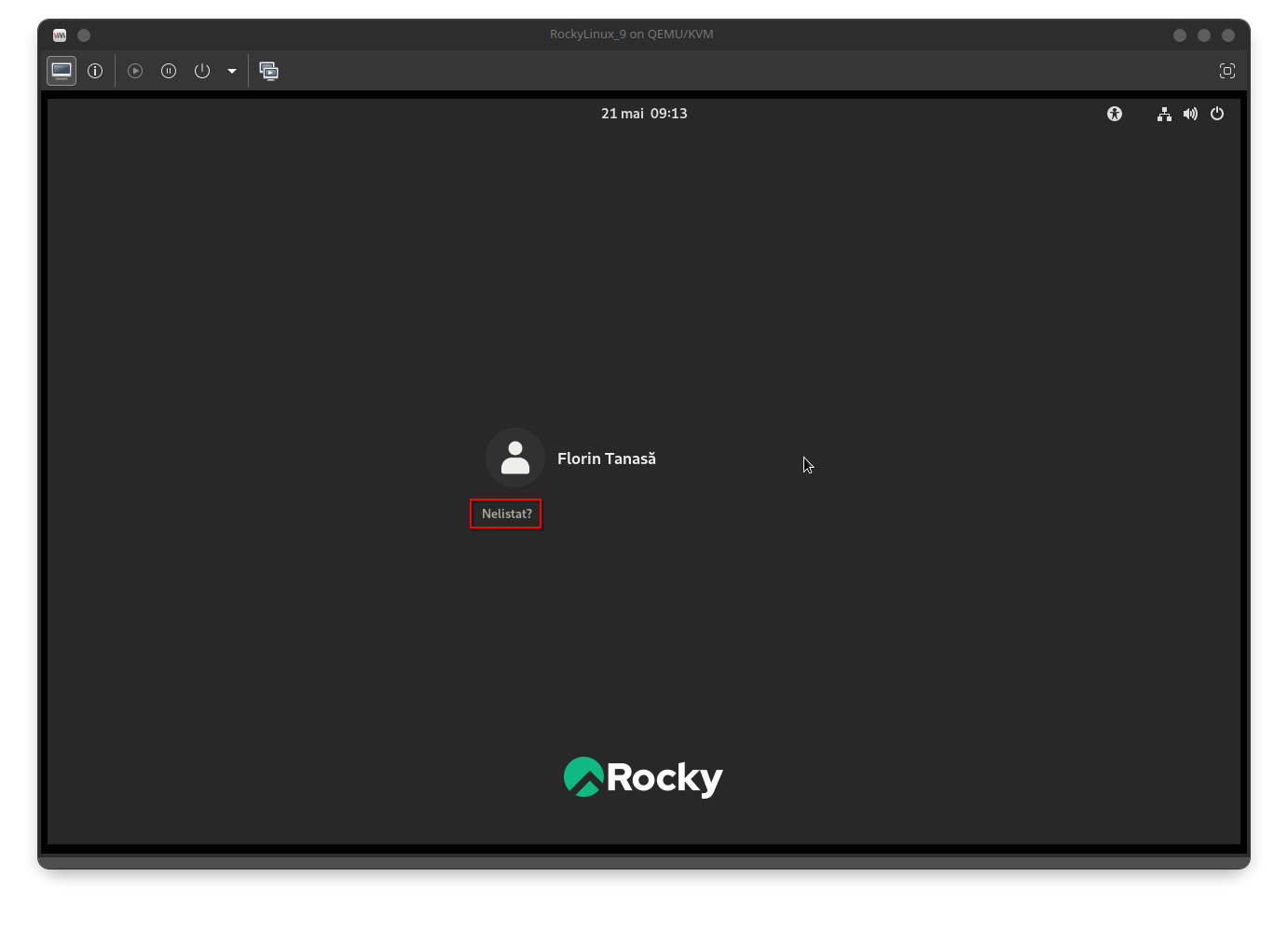
For initial domain authentication, select the user Not listed?:
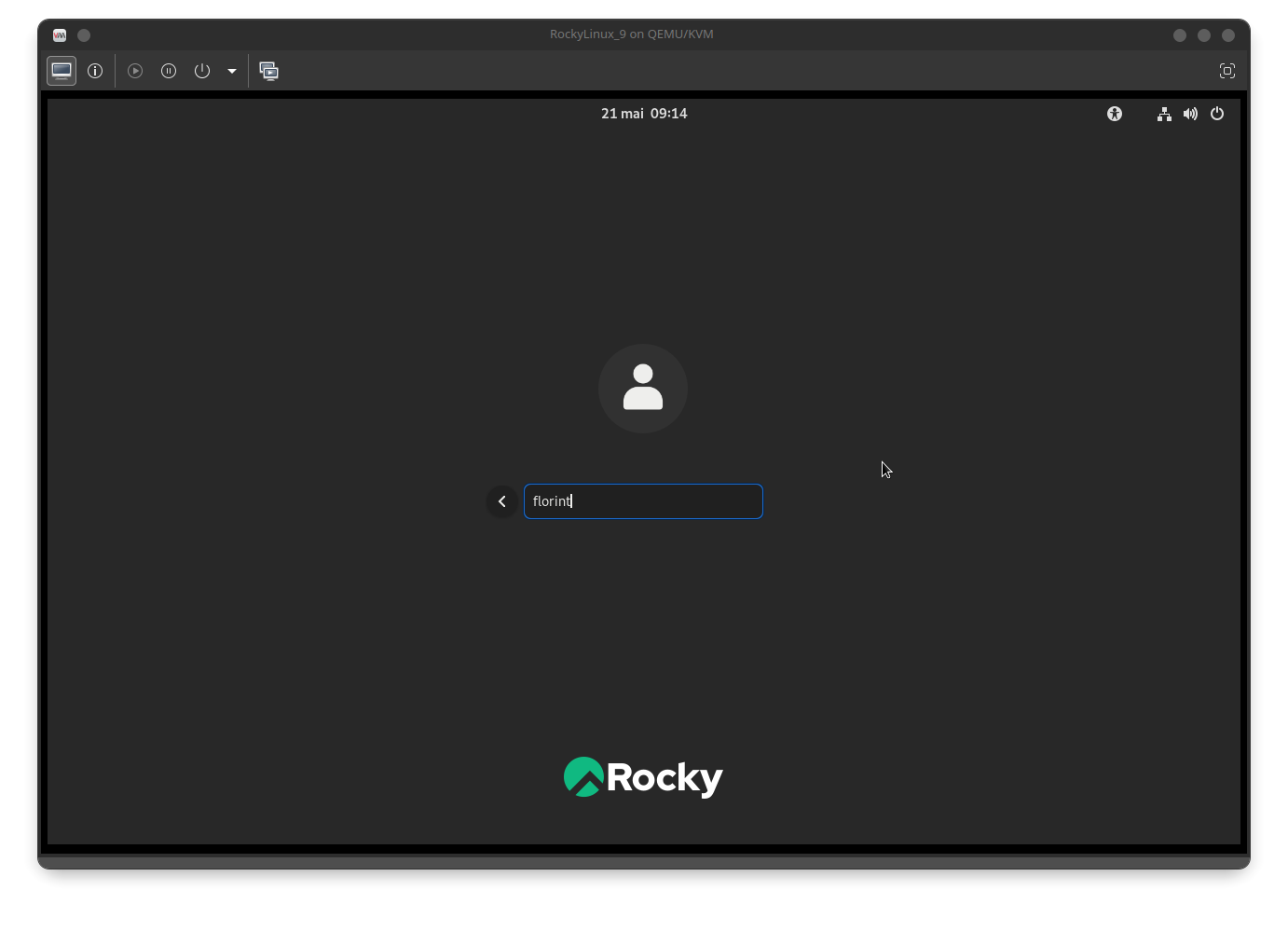
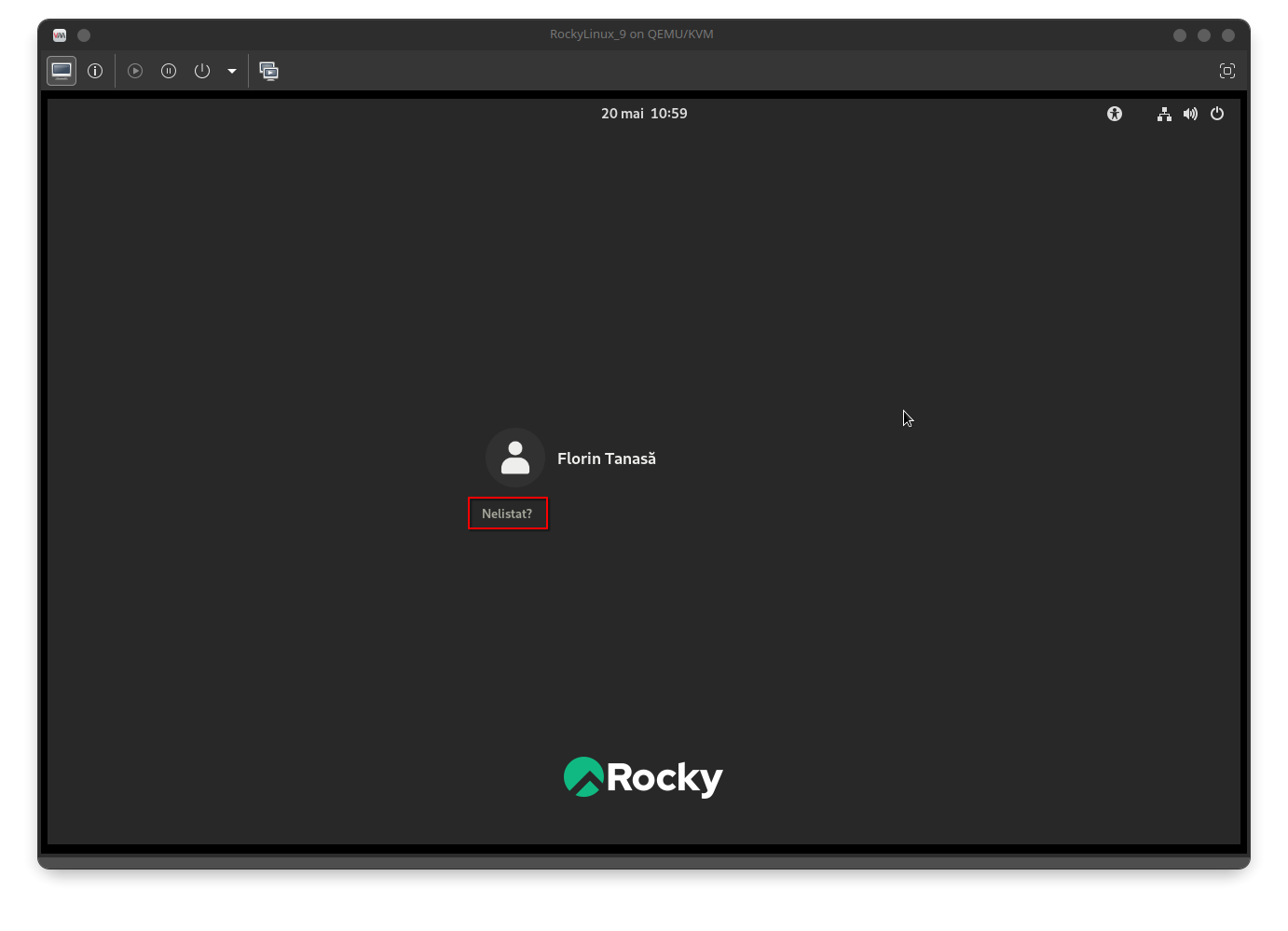 Then enter the domain username:
Then enter the domain username:
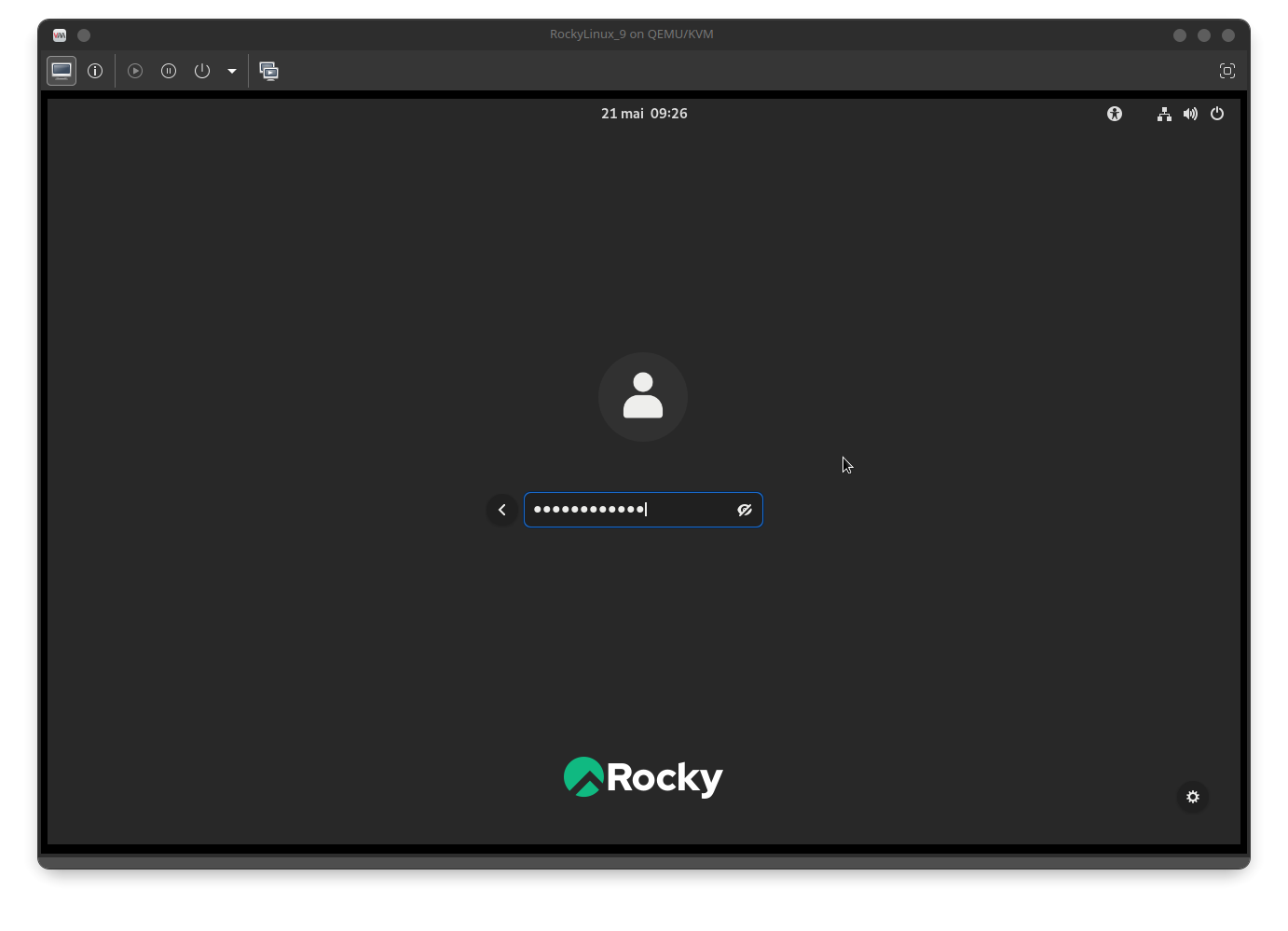
 Finally, enter the domain user's password:
Finally, enter the domain user's password:
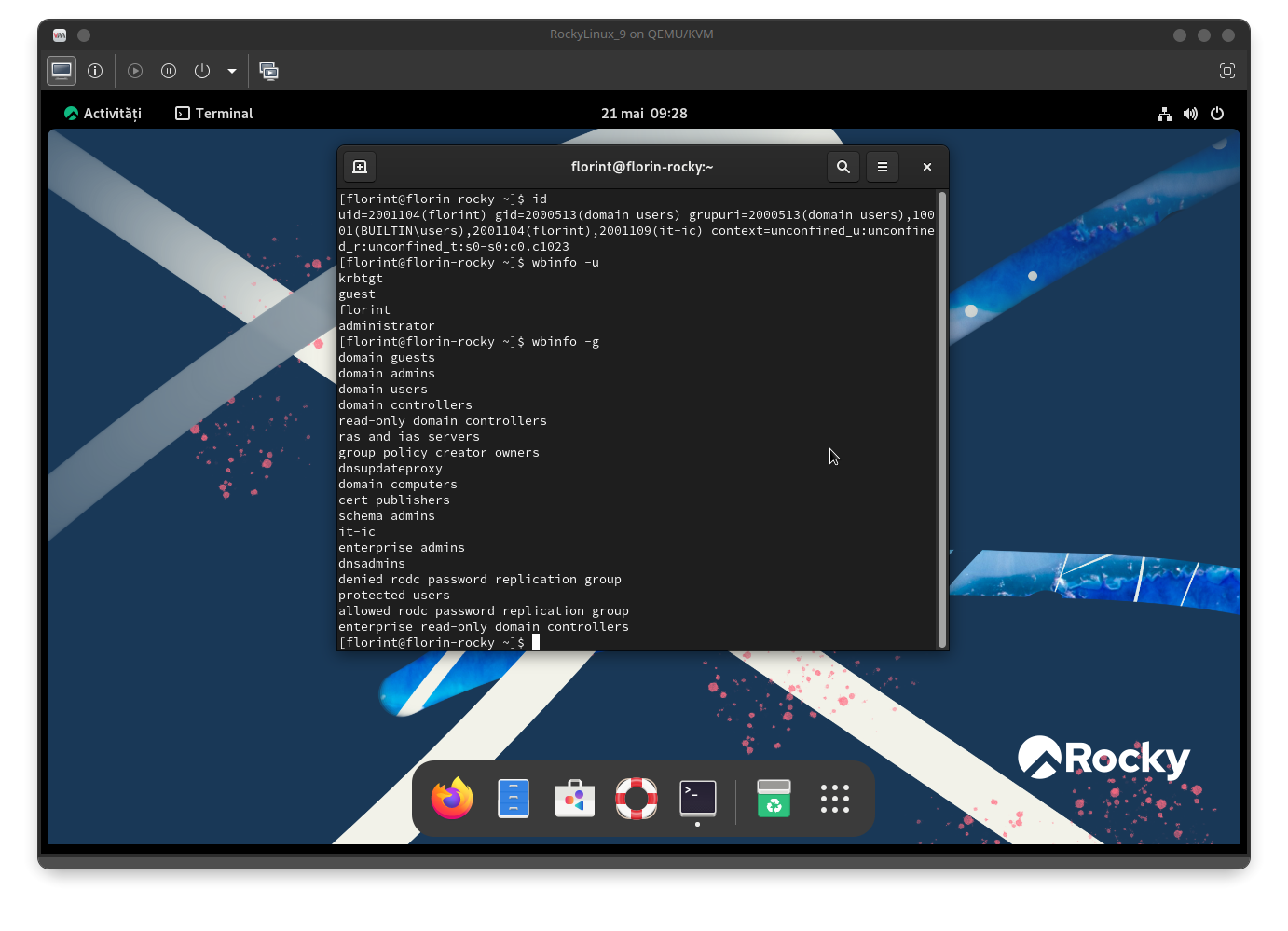
 After authenticating to the domain, you will be connected and the workstation will be operational:
After authenticating to the domain, you will be connected and the workstation will be operational:
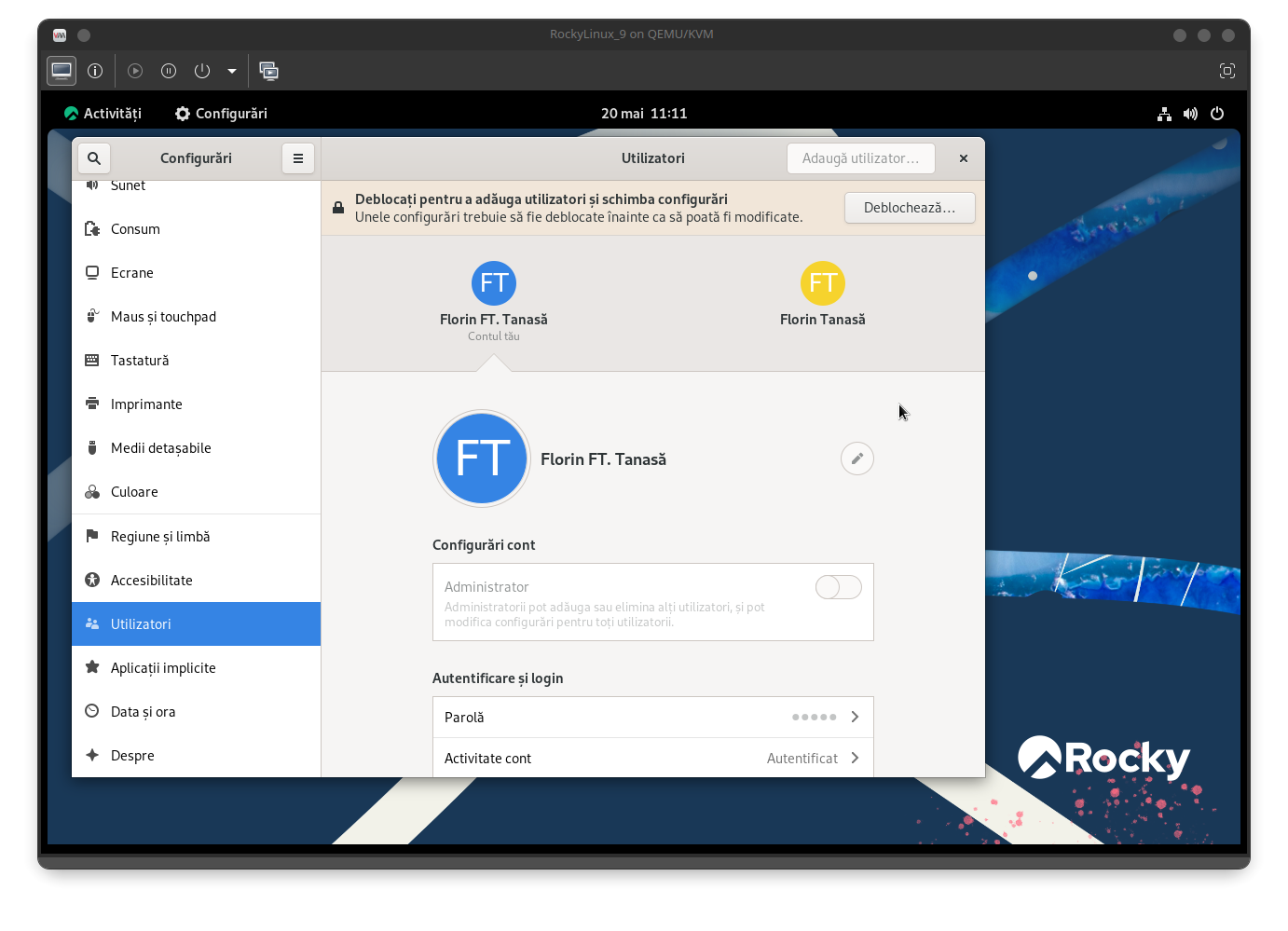 As shown, the workstation has retrieved information from the AD-DC.
As shown, the workstation has retrieved information from the AD-DC.
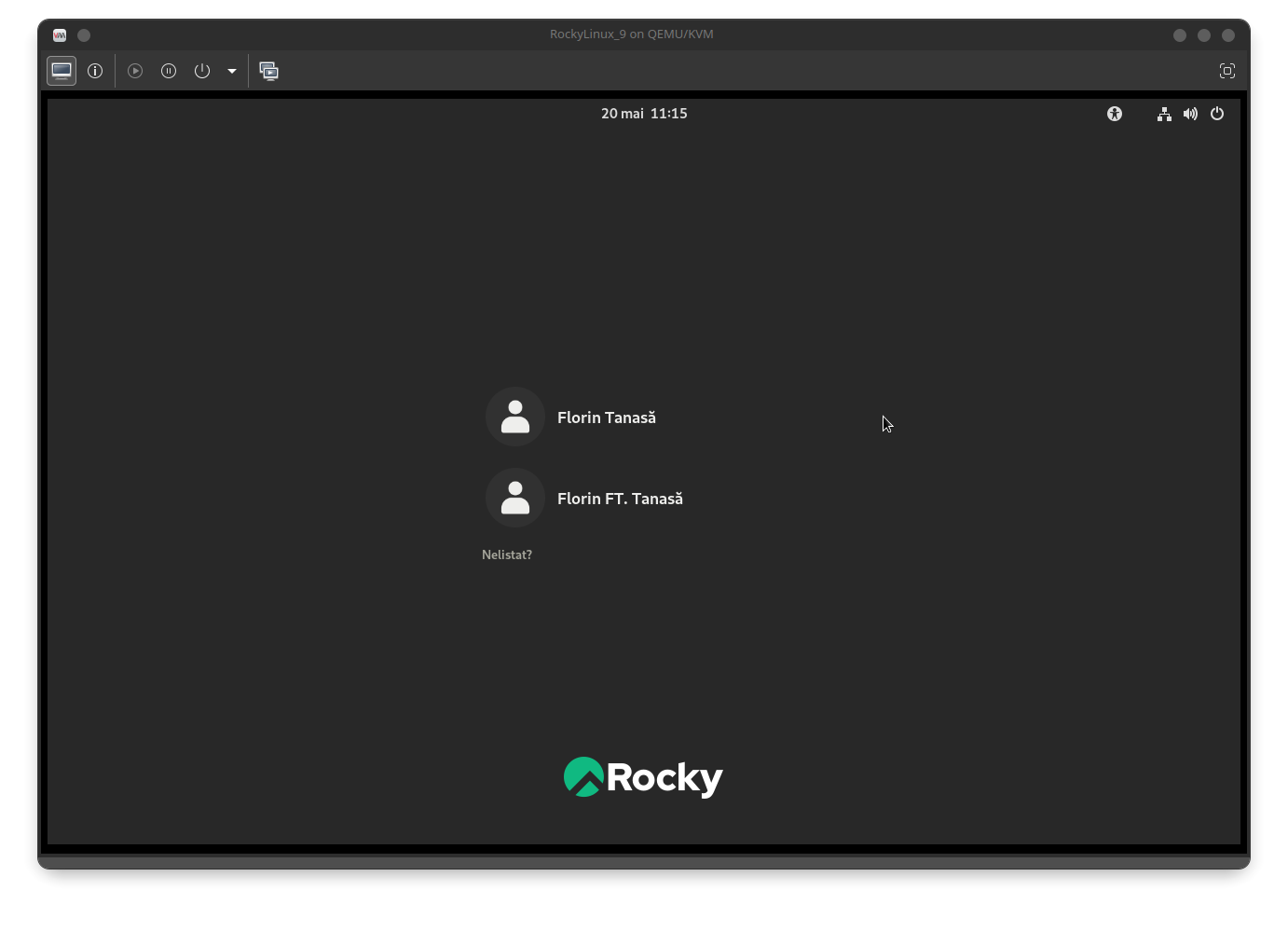
User florint will be visible at the next login in the desktop manager (GDM):
Removing a workstation from the domain
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo realm leave svgenebank.lanEnrollment method using Samba and Winbind services
Next, the machine florin-rocky will be enrolled using Samba and Winbind. This is the preferred method:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo dnf install samba samba-winbind samba-client
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo realm join -v --membership-software=samba --client-software=winbind dc1.svgenebank.lanVerify that the services winbind, and oddjobd are running:
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo systemctl status winbind.service
● winbind.service - Samba Winbind Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/winbind.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-05-21 08:18:29 EEST; 3min 45s ago
Docs: man:winbindd(8)
man:samba(7)
man:smb.conf(5)
Main PID: 3389 (winbindd)
Status: "winbindd: ready to serve connections..."
Tasks: 6 (limit: 16182)
Memory: 17.6M
CPU: 795ms
CGroup: /system.slice/winbind.service
├─3389 /usr/sbin/winbindd --foreground --no-process-group
├─3392 /usr/sbin/winbindd --foreground --no-process-group
├─3394 /usr/sbin/winbindd --foreground --no-process-group
├─3604 /usr/libexec/samba/samba-dcerpcd --libexec-rpcds --ready-signal-fd=24 --np-helper --debuglevel=0
├─3614 /usr/libexec/samba/rpcd_lsad --configfile=/etc/samba/smb.conf --worker-group=6 --worker-index=5 --debuglevel=0
└─3616 /usr/libexec/samba/rpcd_lsad --configfile=/etc/samba/smb.conf --worker-group=6 --worker-index=6 --debuglevel=0
mai 21 08:18:30 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3468]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky samba-dcerpcd[3604]: [2025/05/21 08:21:26.801281, 0] ../../source3/rpc_server/rpc_host.c:2905(main)
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky samba-dcerpcd[3604]: samba-dcerpcd version 4.20.2 started.
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky samba-dcerpcd[3604]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3614]: [2025/05/21 08:21:26.940341, 0] ../../source3/rpc_server/rpc_worker.c:1155(rpc_worker_main)
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3614]: rpcd_lsad version 4.20.2 started.
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3614]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3616]: [2025/05/21 08:21:26.971334, 0] ../../source3/rpc_server/rpc_worker.c:1155(rpc_worker_main)
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3616]: rpcd_lsad version 4.20.2 started.
mai 21 08:21:26 florin-rocky rpcd_lsad[3616]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024
[florin@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo systemctl status oddjobd.service
● oddjobd.service - privileged operations for unprivileged applications
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/oddjobd.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-05-21 08:07:26 EEST; 14min ago
Main PID: 913 (oddjobd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 16182)
Memory: 1.3M
CPU: 2ms
CGroup: /system.slice/oddjobd.service
└─913 /usr/sbin/oddjobd -n -p /run/oddjobd.pid -t 300
mai 21 08:07:26 florin-rocky systemd[1]: Started privileged operations for unprivileged applications.Modify the configuration file /etc/samba/smb.conf so that at login the user is used instead of user@domain_name, and enable the ability to retrieve the list of users and groups:
winbind use default domain = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
winbind enum users = yesThe file will have the following structure:
# See smb.conf.example for a more detailed configuration file or
# Read the smb.conf manpage.
# Run 'testparm' to verify that the configuration is correct after
# modifying it.
#
# Note:
# SMB1 is disabled by default. This means clients without support for SMB2 or
# SMB3 can no longer connect to smbd (by default).
[global]
security = ads
passdb backend = tdbsam
printing = cups
printcap name = cups
load printers = yes
cups options = raw
kerberos method = secrets and keytab
template homedir = /home/%U@%D
password server = dc1.svgenebank.lan
template shell = /bin/bash
idmap config SVGENEBANK : range = 2000000-2999999
idmap config SVGENEBANK : backend = rid
idmap config * : range = 10000-999999
idmap config * : backend = tdb
winbind use default domain = yes
winbind refresh tickets = yes
winbind offline logon = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
winbind enum users = yes
realm = SVGENEBANK.LAN
workgroup = SVGENEBANK
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
valid users = %S, %D%w%S
browseable = No
read only = No
inherit acls = Yes
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/tmp
printable = Yes
create mask = 0600
browseable = No
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/drivers
write list = @printadmin root
force group = @printadmin
create mask = 0664
directory mask = 0775To grant the user florint permission to run any command and administer the machine, they must be added to the /etc/sudoers file:
# Users from the domain allowed to run all commands
florint ALL=(ALL) ALLLogging into a domain machine can be performed using the domain username:
 To be visible on the network and share files, start the
To be visible on the network and share files, start the samba service:
[florint@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo systemctl start smb.service
[florint@florin-rocky ~]$ sudo systemctl status smb.service
● smb.service - Samba SMB Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/smb.service; disabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-05-21 09:16:17 EEST; 5min ago
Docs: man:smbd(8)
man:samba(7)
man:smb.conf(5)
Main PID: 3030 (smbd)
Status: "smbd: ready to serve connections..."
Tasks: 4 (limit: 16182)
Memory: 9.5M
CPU: 399ms
CGroup: /system.slice/smb.service
├─3030 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
├─3032 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
├─3033 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
└─3045 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
mai 21 09:16:17 florin-rocky systemd[1]: Started Samba SMB Daemon.
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky samba-dcerpcd[3047]: [2025/05/21 09:16:34.047253, 0] ../../source3/rpc_server/rpc_host.c:2905(main)
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky samba-dcerpcd[3047]: samba-dcerpcd version 4.20.2 started.
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky samba-dcerpcd[3047]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky rpcd_classic[3057]: [2025/05/21 09:16:34.199873, 0] ../../source3/rpc_server/rpc_worker.c:1155(rpc_worker_main)
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky rpcd_classic[3057]: rpcd_classic version 4.20.2 started.
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky rpcd_classic[3057]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky rpcd_winreg[3059]: [2025/05/21 09:16:34.231102, 0] ../../source3/rpc_server/rpc_worker.c:1155(rpc_worker_main)
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky rpcd_winreg[3059]: rpcd_winreg version 4.20.2 started.
mai 21 09:16:34 florin-rocky rpcd_winreg[3059]: Copyright Andrew Tridgell and the Samba Team 1992-2024The machine will now be visible:
 The station
The station florin-rocky can be accessed by any domain user. Upon the first local or remote login, the directory /home/username@domain_name will be created automatically.
Add a new user on the dc1 server:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool user add alinat --given-name=Alina --surname=Tanasă --initials=AT --mail-address=alina.tanasa@genebanksv.ro --job-title='Scientific researcher' --department='In Vitro' --company='Genebank Suceava'--internet-address=genebanksv.ro --login-shell=/bin/bash
New Password:
Retype Password:
User 'alinat' added successfullyThen create a new group and add the user alinat to it:
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group add "Scientific researchers" --description='Group for scientific researchers members' --mail-address=researchers@genebanksv.ro
Added group Scientific researchers
florin@dc1:~$ sudo samba-tool group addmembers "Scientific researchers" alinat
Added members to group Scientific researchers
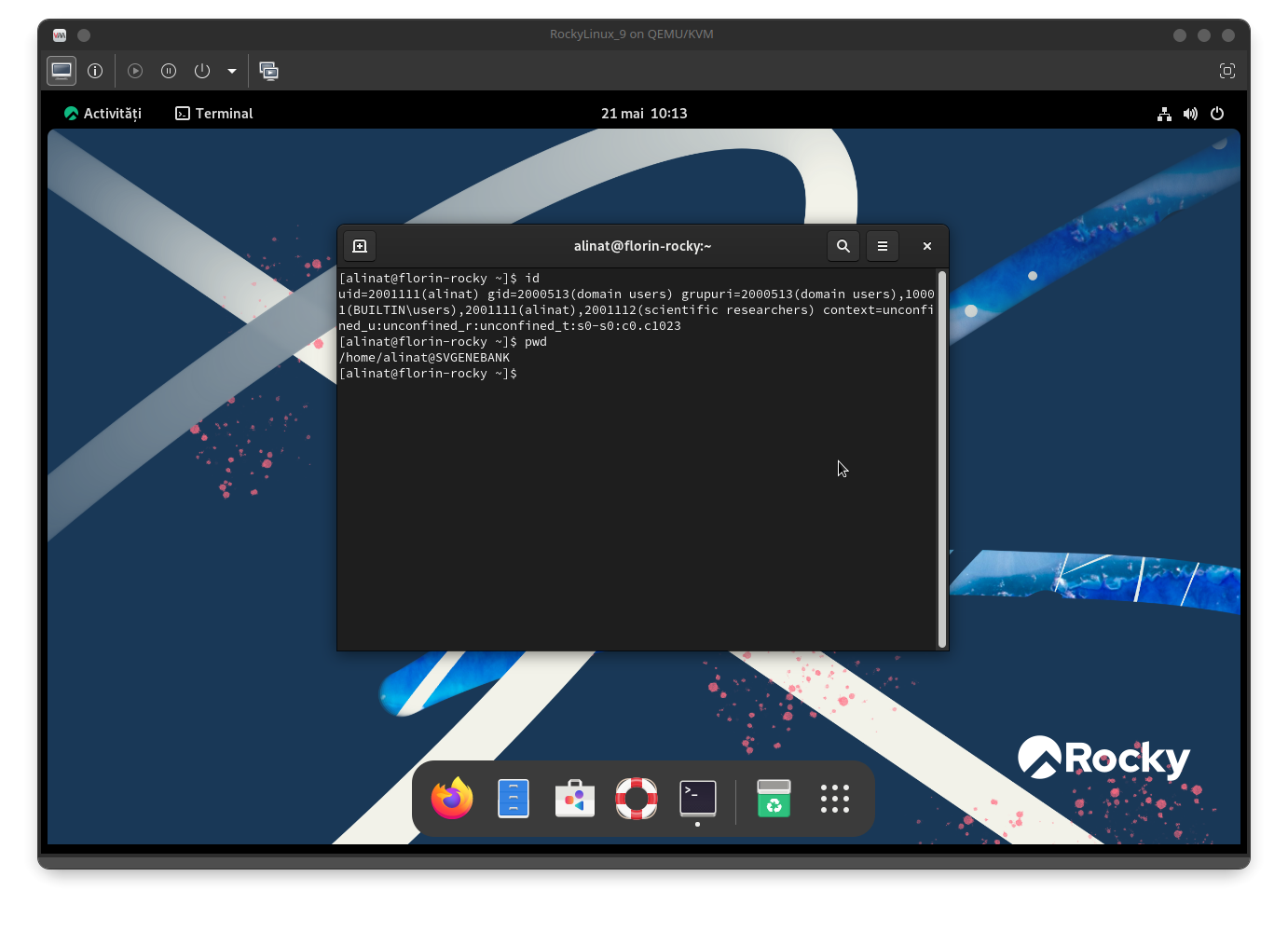
florin@dc1:~$The user alinat can now connect to any station within the domain, using either local login or remote connection via ssh:
florin@dc1:~$ ssh alinat@florin-rocky.svgenebank.lan
alinat@florin-rocky.svgenebank.lan's password:
[alinat@florin-rocky ~]$ id
uid=2001111(alinat) gid=2000513(domain users) grupuri=2000513(domain users),10001(BUILTIN\users),2001111(alinat),2001112(scientific researchers) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
[alinat@florin-rocky ~]$ pwd
/home/alinat@SVGENEBANK
[alinat@florin-rocky ~]$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp1s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:69:85:39 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.41/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global noprefixroute enp1s0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fe69:8539/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[alinat@florin-rocky ~]$ hostname -f
florin-rocky.svgenebank.lanAlthough the user alinat has not yet logged in locally, the account has been created on the florin-rocky station:
| List of local and domain users | Working directory and user ID |
 |
 |